Stem Cell Applications
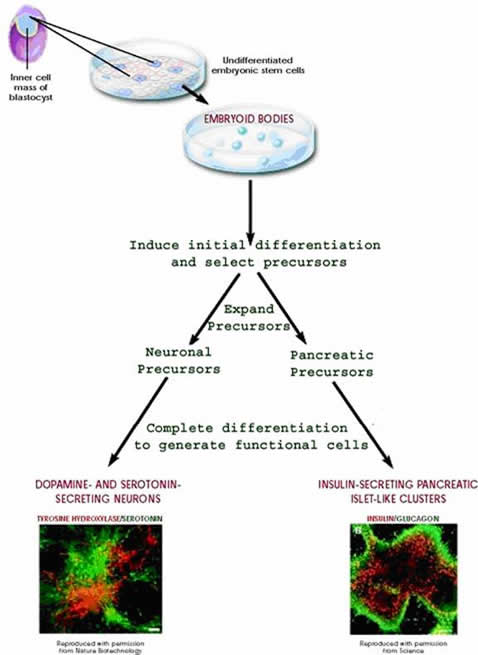 The creation of synthetic organs is complex and has multiple different techniques. However, the basis of these methods lies with the manipulation of stem cells. Because stem cells have the power to differentiate into desired cells, scientists can use them to create different synthetic organs (7).
The creation of synthetic organs is complex and has multiple different techniques. However, the basis of these methods lies with the manipulation of stem cells. Because stem cells have the power to differentiate into desired cells, scientists can use them to create different synthetic organs (7).
In order to differentiate the stem cells into the desired cell, they must begin to cluster into embryoid bodies. The differentiation is controlled by scientists by changing certain factors in the cell's controlled environment, such as the chemical composition or the culture dish surface. They may also spur the differentiation by injecting the specific genetics for their particular need. The stem cell can then begin to grow into the desired type of cell (8).
Stem Cell Differentiation
 The structures in which the differentiated cells are placed are called scaffolds. Scaffolds can be either two-dimensional or three-dimensional, though 3-D scaffolds are preferred. These scaffolds are created from fragments of amino acids. These amino acids are then arranged into nanofibers, pictured to the right, in which the cells are placed. These scaffolds work better than the traditional petri dishes because, due to their structure and makeup, they better represent the natural environments of cells (9).
The structures in which the differentiated cells are placed are called scaffolds. Scaffolds can be either two-dimensional or three-dimensional, though 3-D scaffolds are preferred. These scaffolds are created from fragments of amino acids. These amino acids are then arranged into nanofibers, pictured to the right, in which the cells are placed. These scaffolds work better than the traditional petri dishes because, due to their structure and makeup, they better represent the natural environments of cells (9).
Other Potential Methods
Because simply growing stem cells into organs has not yet been perfected, additional methods have also been introduced.
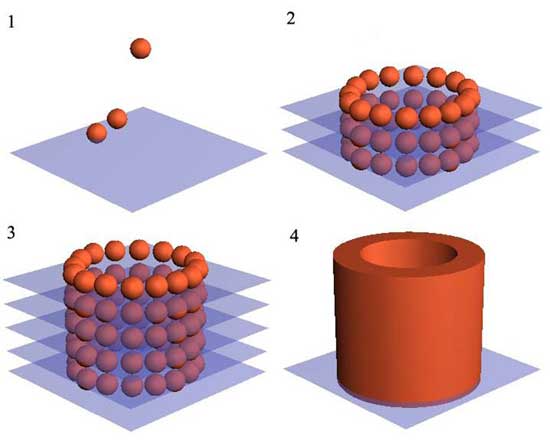 [ Bioprinting ]
[ Bioprinting ]
Bioprinting is the computer-aided, automatic, layer-by-layer deposition, transfer, and patterning of biologically relevant materials (10). This technique was created by Gabor Forgacs of the University of Missouri-Columbia and colleagues.It employs the use of a bioprinter, which is similar to ink-jet printers, and bio-ink in order to "print" cells into the three-dimensional organ modules that can be used as grafts for creating organs. Using this method, scientists can avoid the risk of organ rejection by patients because of the use of their own cells (11).